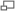Built in Beams II
Shear and Deflection formulae for Built in and Continuous Beams.
Contents
- Introduction
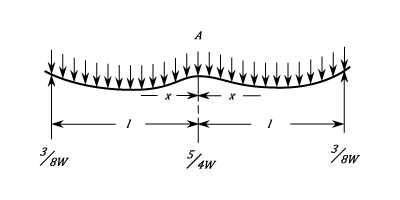
- Fixed At Both Ends. Uniform Load. Total Load W
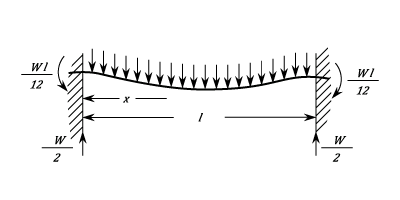
- Fixed At Both Ends. Load At Centre.
- Fixed At Both Ends. Load At Any Point.
- Continuous Beam With Two Equal Spans. Uniform Load
- A Continuous Beam With Two Unequal Spans And Unequal Uniform Loads.
- A Continuous Beam With Two Unequal Spans With Two Unequal Loads At Any Point On Each
- Page Comments
Introduction
See Also the section on "Built in Beams" . Revisiting the definition, a Beam is said to be Built-in or 'encastre' when both ends are rigidly fixed so that the slope at both ends can be assumed to be zero. In this section we present the solutions for the stress and deflection in a built in and continuous beam due to either uniform or point loads. With each solution the following definitions apply:is the bending at any point
is the section module of the beam cross-section, equal to
where
is the distance from the beam centroid to the top or bottom edge of the beam.
is the deflection at any point
is the load on the beam
is the modulus of elasticity
is the moment of inertia for the cross section about the neutral axis
Fixed At Both Ends. Uniform Load. Total Load W
The stress at any Point : ^2\right\}) The Maximum Stress is at the ends and is
The Maximum Stress is at the ends and is  The Stress is zero at
The Stress is zero at  and
and  The Greatest negative Stress is at the centre and is
The Greatest negative Stress is at the centre and is  The Deflection at any Point is given by
The Deflection at any Point is given by ^2) The Maximum Deflection is at the Centre and is
The Maximum Deflection is at the Centre and is 
Deflection is a term that is used to describe the degree to which a structural element is displaced under a load.
Fixed At Both Ends. Load At Centre.
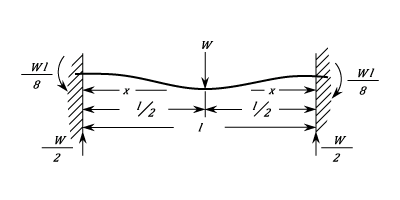
The Stress between each end and the Load: ) The Stress at each end is :
The Stress at each end is :  The Stress at the middle is:
The Stress at the middle is:  These are the maximum Stresses and are equal and opposite.
The stress is zero at
These are the maximum Stresses and are equal and opposite.
The stress is zero at  The Deflection at any point is given by:
The Deflection at any point is given by: ) The Maximum Deflection is at the Load and is:
The Maximum Deflection is at the Load and is: 
Fixed At Both Ends. Load At Any Point.
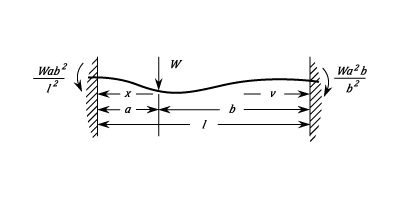
The Stress at any Point within the segment of length  :
:
) The Stress at any point within the segment of length
The Stress at any point within the segment of length  :
:
) The Stress at the end next to segment of length
The Stress at the end next to segment of length  :
:  The Stress at the end next to segment of length
The Stress at the end next to segment of length  :
:  The Maximum Stress is at the end next to the shorter segment.
The Stress is Zero for:
The Maximum Stress is at the end next to the shorter segment.
The Stress is Zero for:  and
and  The Greatest negative stress is at the Load and is given by:
The Greatest negative stress is at the Load and is given by:  The Deflection for the segment of length
The Deflection for the segment of length  is given by:
is given by:
&space;+&space;l(a&space;-&space;x)) The Deflection for the segment of length
The Deflection for the segment of length  is given by:
is given by:
&space;+&space;l(b&space;-&space;v)) The deflection at the Load is:
The deflection at the Load is:  Let
Let  be the length of the longer segment and
be the length of the longer segment and  the shorter one.
The Maximum Deflection is in the longer Segment and occurs at
the shorter one.
The Maximum Deflection is in the longer Segment and occurs at 
})
A beam is a horizontal structural element that is capable of withstanding load primarily by resisting bending. The bending force induced into the material of the beam as a result of the external loads, own weight, span and external reactions to these loads is called a bending moment.
The Stress at any Point is given by: }{2\;Z\;l}\;\;\left(\displaystyle\frac{1}{4}l&space;-&space;x&space;\right)) The Maximum Stress is at Point
The Maximum Stress is at Point  and is:
and is:  The Stress is zero at
The Stress is zero at  The greatest negative Stress is at
The greatest negative Stress is at  and is:
and is:  The Deflection at any Point is given by:
The Deflection at any Point is given by: }{48\;E\;I\;l}\;\;(3l&space;-&space;2x)) The Maximum Deflection is at
The Maximum Deflection is at  and is given by:
and is given by:  The Deflection at the centre of each Span is:
The Deflection at the centre of each Span is:  The Deflection at the point of greatest negative Stress at
The Deflection at the point of greatest negative Stress at  is
is 
A Continuous Beam With Two Unequal Spans And Unequal Uniform Loads.
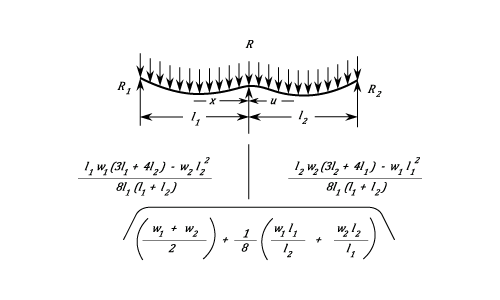
Between  and
and  The Stress is given by:
The Stress is given by: \;W_1&space;}{2\;l_1}&space;-&space;R_1\right\})
Between and
and  The Stress is given by:
The Stress is given by: \;W_2}{2\;l_2}&space;&space;-&space;R_2\right\}) Stress at the Support
Stress at the Support  is:
is: }) The greatest Stress in the first span is at:
The greatest Stress in the first span is at: ) And is
And is  The greatest Stress in the second Span is at:
The greatest Stress in the second Span is at: ) And is
And is  The Deflection between
The Deflection between  is given by:
is given by:
}{24\;E\;I}\left\{(2l_1&space;-&space;x)(4R_1&space;-&space;W_1)&space;-&space;\frac{W_1\;(l_1&space;-&space;x)^2}{l_1}&space;\right\}) The Deflection between
The Deflection between  is given by:
is given by:
}{24\;E\;I}\left\{(2l_2&space;-&space;u)(4R_2&space;-&space;W_2)&space;-&space;\frac{W_2\;(l_2&space;-&space;u)^2}{l_2}&space;\right\}) The above example is so complicated that convenient general expressions for the maximum deflections cannot be obtained
The above example is so complicated that convenient general expressions for the maximum deflections cannot be obtained
Between
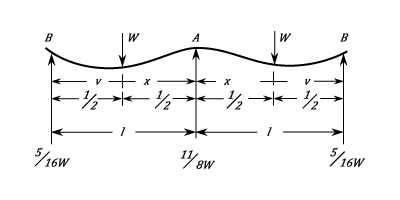
Between point  and the Load the Stress at any Point is:
and the Load the Stress at any Point is: ) Between Point
Between Point  and the Load the stress at any Point
and the Load the stress at any Point  The Maximum Stress at Point
The Maximum Stress at Point 
 The Stress is Zero at:
The Stress is Zero at:  The greatest negative Stress is at the centre of the Span and is:
The greatest negative Stress is at the centre of the Span and is:
 Between Point
Between Point  and the Load the Deflection at any point is:
and the Load the Deflection at any point is:
) Between Point
Between Point  and the Load the Deflection at any point is:
and the Load the Deflection at any point is:
) The Maximum deflection at
The Maximum deflection at  is:
is:  The Deflection at the Load is:
The Deflection at the Load is: 
A Continuous Beam With Two Unequal Spans With Two Unequal Loads At Any Point On Each
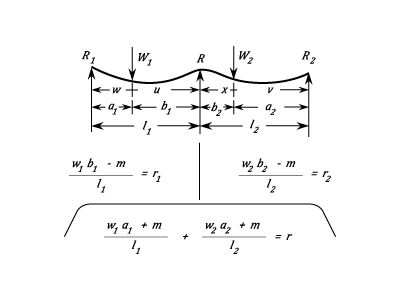
Between  and
and  the Stress is:
the Stress is:  Between
Between  and
and  the Stress is:
the Stress is: &space;-&space;W_1\;a_1\;u]) Between
Between  and
and  the Stress is:
the Stress is: &space;-&space;W_2\;a_2\;x]) Between
Between  and
and  the Stress is:
the Stress is:  Stress at the Load:
Stress at the Load:  Where,
Where,
}\;\;\left(\frac{w_1\;a_1\;b_1}{l_1}\;(l_1&space;+&space;a_1)&space;+&space;\frac{w_2\;a_2\;b_2}{l_2}\;\;(l_2&space;+&space;a_2)&space;\right)) Stress at Support
Stress at Support  :
:  Stress at load
Stress at load  :
:  The greatest of these is the maximum Stress.
The Deflection between
The greatest of these is the maximum Stress.
The Deflection between  and
and 
(l_1&space;+&space;w)r_1&space;-&space;\frac{W_1\;b_1^3}{l_1}&space;\right\}) The Deflection between
The Deflection between  and
and 
&space;-&space;W_1\;a_1\;u^2&space;-&space;m(2\;l_1&space;-&space;u)(l_1&space;-&space;u)]) The Deflection between
The Deflection between  and
and 
&space;-&space;W_2\;a_2\;x^2&space;-&space;m(2\;l_2&space;-&space;x)(l_2&space;-&space;x)]) The Deflection between
The Deflection between  and
and 
(l_2&space;+&space;v)r_2&space;-&space;\frac{W_2\;b_2^3}{l_2}&space;\right\}) The Deflection at Load
The Deflection at Load  :
: ]) The Deflection at Load
The Deflection at Load  :
: ])
 Login
Login